fmcg distribution business model
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) distribution is the backbone of the consumer goods industry, as it involves the distribution and delivery of everyday items to the end consumer. The FMCG distribution business model is based on efficient supply chain management, strong distribution networks, and effective customer relationship management.
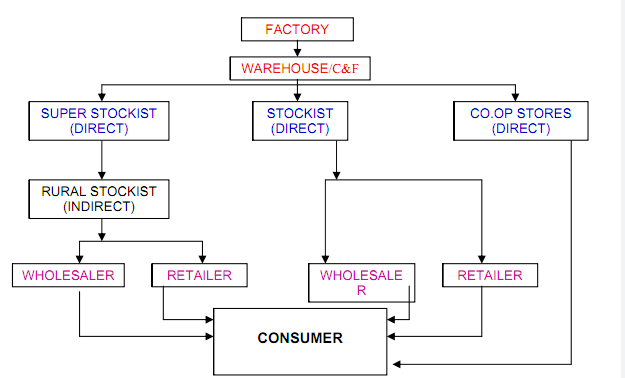
The first step in the FMCG distribution business model is sourcing and procurement of products. FMCG companies typically source their products from manufacturers and suppliers and then store them in warehouses for distribution to retailers. The procurement process is critical as it involves negotiations with suppliers, contracts, and inventory management.
Once the products have been sourced, the next step is to distribute them to retailers, which can be done through a variety of channels, including direct sales, wholesalers, and distributors. Direct sales involve selling products directly to retailers, while wholesalers and distributors act as intermediaries, purchasing products from the manufacturer and then selling them to retailers.
The next step in the FMCG distribution business model is to manage the supply chain effectively. This involves ensuring that the right products are delivered to the right places at the right time and in the right quantities. To achieve this, FMCG companies use advanced technology and software to track inventory levels, order fulfillment, and delivery times.
Once the products have reached the retailer, the next step is to manage customer relationships. This involves building strong relationships with retailers, understanding their needs, and offering support and services to help them sell the products effectively. FMCG companies may also offer training and marketing support to help retailers increase sales and market share.
Finally, the last step in the FMCG distribution business model is to measure and analyze the performance of the distribution network. This involves monitoring sales figures, analyzing customer feedback, and evaluating the efficiency of the supply chain. Based on this information, FMCG companies can make changes and improvements to the distribution network to increase efficiency and profitability.
In conclusion, the FMCG distribution business model is a complex and challenging one, but it is essential to the success of the consumer goods industry. FMCG companies must be agile and adaptable, as they need to respond quickly to changes in consumer demand and market conditions. A strong distribution network, effective supply chain management, and strong relationships with retailers are all key components of a successful FMCG distribution business.